Servlet Lifecycle
Servlet Life Cycle
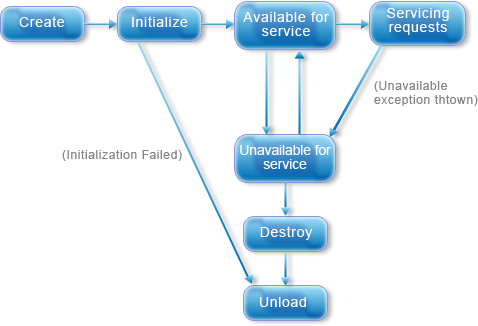
The life cycle of the servlet is controlled by the Servlet container.
Basically there are three methods in servlet lyfe
cycle which servlet calls
1.
init()- This
method is called to initialize a servlet. In servlet 2.4 specification if
you do not call init() method in your servlet program then the container call
it implicitly.
2.
service()- This
method is called to execute the business logic written in servlet. This is the
method which you must have to override, when you are writing a servlet.
3.
destroy()- This
method is called to finalize the servlet.
Note- The servlet call init() and destroy() method
only once called during its life cycle.
- During
initialization stage of the Servlet life
cycle, the web container initializes the Servlet instance by calling
the init() method,
passing an object implementing the ServletConfig interface.
This configuration object allows the Servlet to access name-valueinitialization parameters from
the web application.
- After
initialization, the Servlet can service client requests. Each request is serviced in its own separate
thread. The web container calls the service() method of the
Servlet for every request. The service() method determines the
kind of request being made and dispatches it to an appropriate method to
handle the request. The developer of the Servlet must provide an
implementation for these methods. If a request for a method that is not
implemented by the Servlet is made, the method of the parent class is
called, typically resulting in an error being returned to the requester.
- Finally,
the web container calls the destroy() method that takes the
Servlet out of service. The destroy() method, likeinit(), is
called only once in the lifecycle of a Servlet.
Therefore, three methods are central to the life
cycle of a Servlet. These are init(), service(), and destroy().
They are implemented by every Servlet and are invoked at specific times by the
server.
The following is a typical user scenario of these methods.
1.
Assume that a user enters a URL to a web browser.
§ The
browser then generates an HTTP request for this URL.
§ This
request is then sent to the appropriate server.
2.
The HTTP request is received by the web
server and forwarded to the Servlet container.
§ The
Servlet container maps this request to a particular Servlet.
§ The
Servlet is dynamically retrieved and loaded into the address space of the
Servlet container.
3.
The Servlet container invokes the init() method
of the Servlet.
§ This
method is invoked only when the Servlet is first loaded into memory.
§ It
is possible to pass initialization parameters to the Servlet so it may
configure itself.
4.
The Servlet container invokes the service() method
of the Servlet.
§ This
method is called to process the HTTP request.
§ You
will see that it is possible for the Servlet to read data that has been
provided in the HTTP request.
§ It
may also formulate an HTTP response for the client.
5.
The Servlet remains in the Servlet
container’s address space and is available to process any other HTTP requests
received from clients.
§ The service() method
is called for each HTTP request.
6.
The Servlet container may, at some
point, decide to unload the Servlet from its memory.
§ The
algorithms by which this decision is made are specific to each Servlet
container.
7.
The Servlet container calls the
Servlet's destroy() method to relinquish any resources such as file
handles that are allocated for the Servlet; important data may be saved to a
persistent store.
8.
The memory allocated for the Servlet and
its objects can then be garbage collected.

The web container calls the destroy() method that takes the Servlet out of service. The destroy() method, likeinit(), is called only once in the lifecycle of a Servlet.thanks for your valuable information.java training in chennai | java training in velachery
ReplyDelete